
Coolfood meals are a delicious way
for you to take action on climate change!
So… what does low carbon mean?
World Resources Institute has established daily carbon allowances for typical meals to help us collectively achieve the 2030 Paris Agreement climate goals.
Every Low Carbon Certified Meal has emissions 38% lower than the average regional meal, ensuring it aligns with these allowances.


These are the carbon allowances we’ve worked out
Maximum Daily Carbon Emissions from Food per person in North America 19kg CO2e
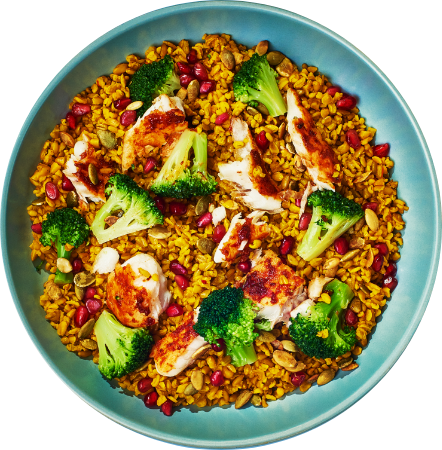

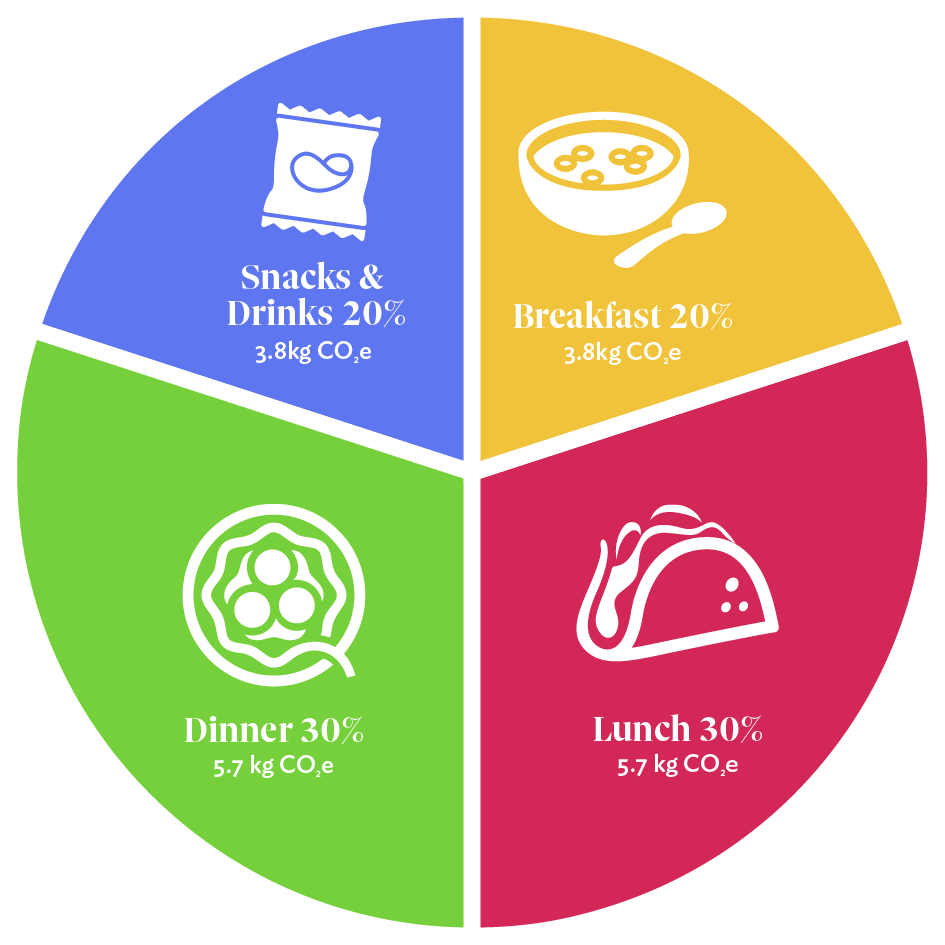

Only the best meals make the grade!
5 steps to become Coolfood certified
1.
Companies submit ingredients and recipes.
2.
Coolfood provide detailed calculations on a per meal basis.
3.
If a meal’s carbon emissions are below the carbon allowances then they are eligible.
4.
Meals are then run through the NutriScore calculator and only recipes in the A, B or C categories are accepted.
5.
Certified meals then get to display Coolfood’s Low Carbon certification mark.
We measure everything
Every ingredient in a Coolfood
meal has been assessed
Coolfood is an initiative of the World Resources Institute and works with its climate and data scientists to create comprehensive carbon calculations. Different foods have a different impact, and these calculations include two key factors:
1.
Analysis of the agricultural supply chain of every ingredient.
2.
Analysis of the land used to produce the ingredients.
Analyzing not just the emissions from farms and food supply chains, but also the consequences of converting land from its natural state to agriculture, provides a more complete picture of the impacts that our food choices have on the climate.
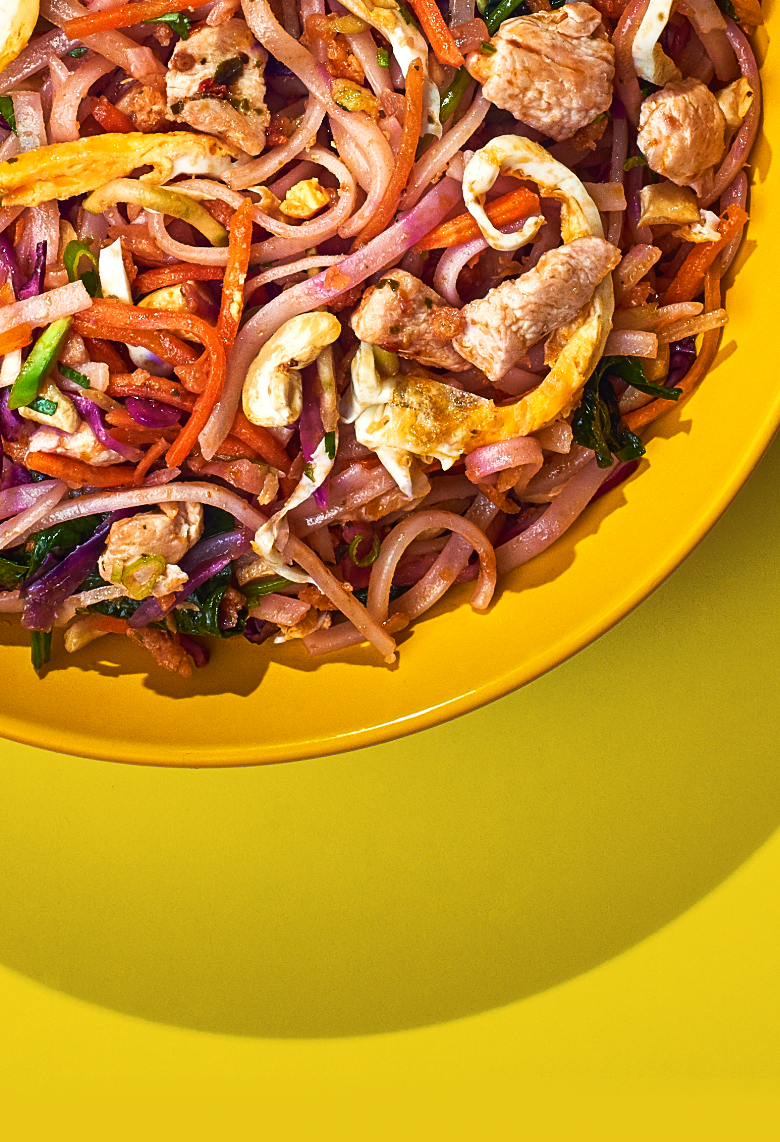

We measure everything
Every ingredient in a Coolfood meal has been assessed
Coolfood is an initiative of the World Resources Institute and works with its climate and data scientists to create comprehensive carbon calculations. Different foods have a different impact, and these calculations include two key factors:
1.
Analysis of the agricultural supply chain of every ingredient.
2.
Analysis of the land used to produce the ingredients.
Analyzing not just the emissions from farms and food supply chains, but also the consequences of converting land from its natural state to agriculture, provides a more complete picture of the impacts that our food choices have on the climate.
Coolfood impact
Trusted by over 80 global organizations, find out how these companies have worked with Coolfood to reduce their carbon emissions.




